
Read more about the causes of rhesus disease. The antibodies can continue attacking the baby's red blood cells for a few months after birth. If she's pregnant with an RhD positive baby, the antibodies can cross the placenta, causing rhesus disease in the unborn baby. If sensitisation occurs, the next time the woman is exposed to RhD positive blood, her body produces antibodies immediately. Sensitisation happens when a woman with RhD negative blood is exposed to RhD positive blood, usually during a previous pregnancy with an RhD positive baby. The woman’s body responds to the RhD positive blood by producing antibodies (infection-fighting molecules) that recognise the foreign blood cells and destroy them. The mother must have also been previously sensitised to RhD positive blood. Rhesus disease only happens when the mother has rhesus negative blood (RhD negative) and the baby in her womb has rhesus positive blood (RhD positive). Read about the symptoms of rhesus disease in a baby. Rhesus disease doesn't harm the mother, but it can cause the baby to become anaemic and develop newborn jaundice. It's also known as haemolytic disease of the foetus and newborn (HDFN).

what causes this? HIV / AIDS questions.Rhesus disease is a condition where antibodies in a pregnant woman's blood destroy her baby's blood cells.
A negative blood type pregnancy complications full#
Rh negative blood and pregnancy complications!! all about rogham shot Lupus and RH Negative My baby has ABO incompatibility, what is that? Blood types in pregnancy RH factor Rh negative blood type and pregnancy Can ABO incompatibility be inherited? conceiving a baby after full term pregnancy with RH negative Rh- negative preganacy What is a Cal (Kal?) Factor and how does it complicate pregn AIHA - Auto Immune Haemolytic Aneamia FATHERS BLOOD, FETUS hemolytic anemia blood transfusion Is there a treatment for ABO incompatibility? Will i too have complications during pregnancy n delivery time like how other Rh negative women? Tranfusion I am RH negative my doc. If the tests show that the baby does not have severe anemia, a normal delivery will be planned and a transfusion can be then carried afterward to ensure that there is no sign of hemolytic anemia. If the fetus is found to be suffering from anemia then an early delivery may have to be planned or a transfusion may have to be done even as the fetus resides inside the uterus. The doctors will take precautions such as regular blood tests to check for anemia in the developing fetus. Is A Second Pregnancy Possible In Case Of Rh Incompatibility?Ī second pregnancy comes with increased risks but it is possible to have a successful pregnancy nonetheless. This factor can only be given before the mother is sensitized to the Rh factor and is useless if given afterward. The doctors can then administer something called ‘RhIg’, which will help destroy any antibodies that form inside the mother. Under normal circumstances, a blood test done during the pregnancy would bring to light the possibility of this reaction occurring. Can Rh Factor Incompatibility Be Treated? In extremely severe cases, this reaction can even be fatal to the fetus. leading to symptoms similar to those seen in asphyxiation. If this response is left unchecked then it can cause a severe lack of oxygen transporting cells in the fetus. To put it simply, the antibodies in the mother’s blood will try and store the red blood cells of the fetus and this can lead to a condition called hemolytic anemia. The second pregnancy, however, is much more dangerous because the next time the fetus and the mother’s blood come into contact, the severity of the immune response will be much more pronounced. This means that the mother is now sensitized against the Rh factor.ĭuring the first pregnancy, the sensitization does not become a big issue because the number of antibodies that have developed in the body is not big enough to cause any significant damage. The mother's blood can come into contact with the fetus’s blood, most commonly during childbirth, and this leads to the formation of antibodies against the Rh factor. In the case of Rh incompatibility, which is when the mother is Rh negative but the child is Rh positive, a number of complications can take place.

However, in 25% of cases, when one of the parents is Rh positive and the other negative, the child can also be Rh negative. The Rh factor is inherited genetically from the parents as a dominant gene and so it commonly requires both parents to be Rh negative for the child to also be Rh negative. It is extremely common in the human population around the world, in fact, almost 85% of the population is considered to be Rh positive, meaning they have the protein.
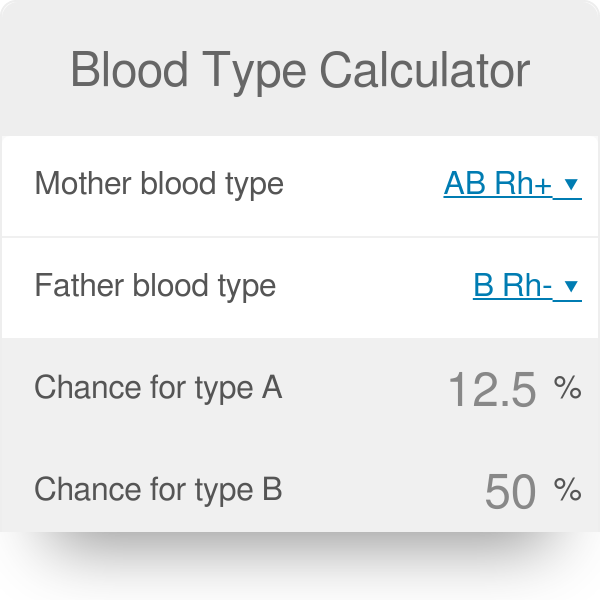
The Rh factor is a protein present on the surface of red blood cells. There is also another factor which helps segregate blood groups called the Rh factor. Blood is divided into groups such as A, B, and O and is that is pretty well known.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
